Lumbar osteoarthritis is one of the most common and most frequently diagnosed types of degenerative joint disease, also known as “sciatica.”The frequency of this disease is extremely large - in about 82% of cases, patients who come to the doctor with the reason of severe back pain are diagnosed with lumbosacral radiculitis.
Disease description
Osteoarthritis in the sacrum or lumbar region occurs with equal frequency in women and men, most commonly in middle age and older.Medical practice shows that this particular disease ranks first among the main causes of temporary or permanent disability and in some cases disability.That is why the treatment of pathology must be extremely cautious, since osteoarthritis can pose a serious danger to human health.

The lumbar region is the name given to the spine consisting of 5 vertebrae designed to connect the sacrum and thoracic region.Lumbar spondylosis is a pathological change in which there is a rapid decrease in flexibility and a change in the natural anatomical structure of the intervertebral discs.Their gradual deformation takes place.
The basis of radiculitis is the slow destruction of the vertebrae, loss of moisture and elasticity, reduced ability to absorb shock.Gradually, the distance between the vertebrae decreases, the disc can harden, leading to nerve roots being compressed.This process is accompanied by severe pain and spasms in the lower back.
How dangerous is osteochondritis, what are its stages?
The progression of the disease is accompanied by degenerative-dystrophic changes, which over time can cause complications such as disc protrusion and herniation.Such degenerative changes may be the main cause of leg paralysis.
Lumbar spondylosis can be accompanied not only by the development of protrusion or herniation of intervertebral discs, but also by other no less serious diseases of internal organs and systems.One of the most common complications is compression of the sciatic nerve, accompanied by severe pain in the lumbar region and numbness in the limbs.
Radiculitis can also cause other serious consequences - vertebral osteoarthritis, bone spurs, spinal degeneration, spinal stenosis, lameness, and scoliosis.The disease can also cause a pathological process in the genital and reproductive sphere;in women, inflammation of the uterus and ovaries;In men, it causes various potency problems.
Lumbar spine degeneration is divided into several stages:
- The first stage of radiculitis is the “mild” stage, in which pain in the lumbar or sacral region remains mild and occurs only with exertion.In the early stages, the process of destruction of the vertebrae is in its early stages.
- The second stage is accompanied by active destruction of the fibrous rings and a decrease in the distance between the vertebrae.This leads to nerve compression and severe pain.
- The third stage - the destruction of the fibrous rings ends, intervertebral hernias appear.The spine is clearly deformed and twisted, losing its normal anatomical shape.
- The fourth stage of the disease is the most serious.At this stage, a person can no longer walk normally;Often the fourth stage ends in disability.
Symptoms of lumbar osteoarthritis
Symptoms and treatment are determined depending on the stage of development of the disease.
In the early stages, as a rule, a person does not pay attention to the first signs of the disease.When turning or walking, the lumbar area may experience mild pain and discomfort.In addition, pain often appears after sitting or standing in one place for a long time.
The main danger of this stage is that the symptoms are still unclear, a person can simply ignore them, as a result of which osteoarthritis progresses rapidly.
The second stage of radiculitis is accompanied by a decrease in the distance between the vertebrae and therefore causes severe pain in the lower back and sacrum, which can spread to the groin and lower limbs.
In the third stage, osteonecrosis is characterized by pronounced symptoms - severe pain, spasms in the back, reduced mobility of the vertebrae and the beginning of pathologies of internal organs and systems.This can lead to problems with the genitourinary system and gynecological inflammation.
Symptoms of the fourth, most severe stage of the disease are manifested in the form of noticeable spinal deformities, possible bending to the side or forward, constant, severe pain, especially aggravated when trying to make any physical movement.Also at this stage, swelling of muscles and ligaments, loss of sensitivity and numbness of the lower limbs may occur.
Modern treatment methods
Osteoarthritis in the lumbosacral spine should be treated - with the help of medications, physiotherapeutic methods, exercise therapy and herbal medicines.In the most severe cases, surgical treatment is used.
Treatment aims to achieve goals such as:
- Reduces pain in the lumbar and sacral areas.
- Eliminates inflammatory processes in the diseased area.
- Eliminates pathological tension in muscle tissue.
- Activates blood circulation in the lumbosacral region of the back.
- Improves mobility of the vertebrae, normalizes sensitivity in the lower limbs.
Treatment with radiculitis drugs is a mandatory element in the complex therapy of osteoarthritis of the lumbar spine.For therapeutic purposes, several drugs are often prescribed:
- Analgesics are used to relieve pain.But we must remember that by eliminating pain, painkillers do not treat the cause of the disease.
- In most cases, doctors prescribe chondroprotective drugs aimed at improving metabolic processes in cartilage fibers and preventing their further deformation.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs - used to eliminate pain and swelling, release compressed nerve endings and reduce the inflammatory process in the affected tissues.
- Drugs belonging to the group of muscle relaxants are used to normalize muscle tone.
- In some cases, medications with a diuretic effect may be prescribed to help reduce swelling in the affected tissues.
- To activate blood circulation in the lumbosacral spine, drugs with vasodilator properties can be prescribed.
- Calcium supplements are commonly used to increase the strength of bone and cartilage tissue.
In the first and second stages of the disease, external drugs are produced in the form of highly effective ointments, creams, lotions.
Traditional method
Traditional medicine offers a variety of different formulas for the effective treatment of osteoarthritis.The most effective methods are considered rubbing, massage and various compresses.But it should be remembered that traditional methods can be effective only in the early stages of the disease.
- One of the most famous recipes is compressed cabbage.To do this, all veins are removed from the surface of the cabbage leaf, then lightly beat the leaf with a hammer and apply it to the underside.The compress is fixed with a wide towel, handkerchief or gauze.Cabbage leaves should be changed several times a day.
- Use a garlic press to grind 3-4 large cloves of garlic, squeeze the juice from the resulting mass through cheesecloth, melt 100 g of lard separately in a water bath.Mix the resulting ingredients in a 1:2 ratio and stir well.The composition is used for massage and massage therapy.
- A spoonful of ground red pepper should be poured into 250 ml of vodka, after which the medicine container should be kept in a dry and dark place for a week.Folk remedies are used for massage.
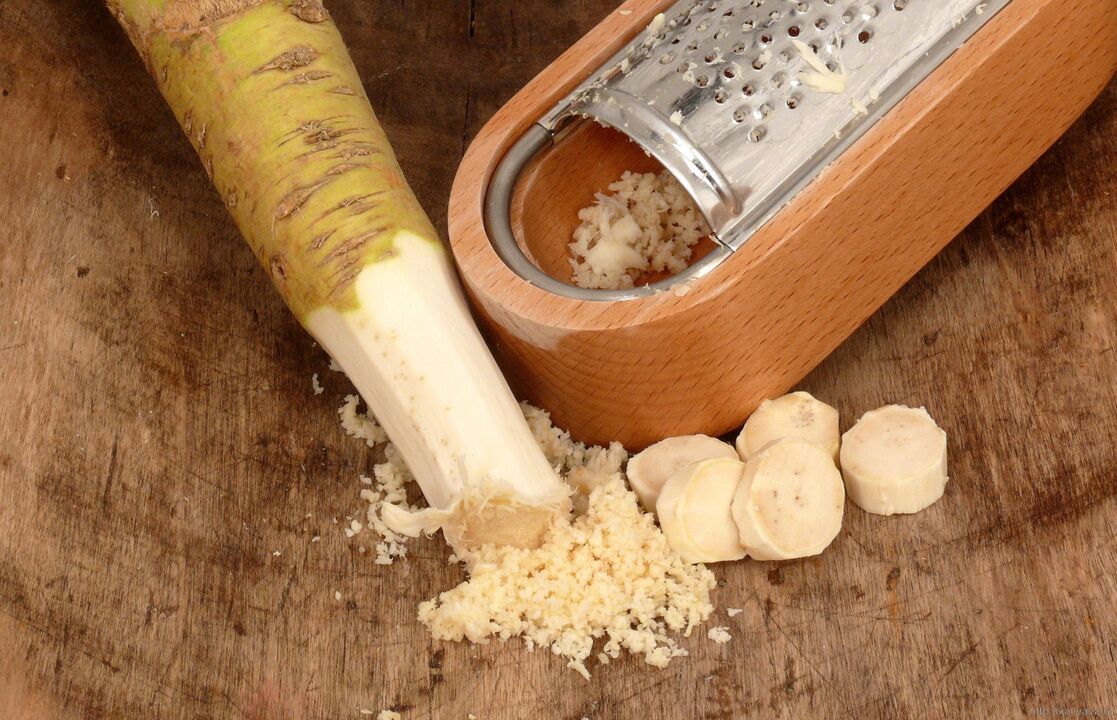
- Horseradish rub is prepared in the same way.Horseradish root, puree, squeeze the juice and mix with the same amount of vodka.This mixture is used for regular rubbing.

Exercise therapy (physical therapy)
Exercise therapy for lumbar spondylosis allows you to eliminate pain, improve the condition of muscle tissue and cartilage, restore spinal mobility, significantly strengthen the musculoskeletal corset and "unload" the lumbar spine.
Exercises for osteoarthritis can be performed only if the patient is not bothered by severe pain in the back.Exercises can be very diverse - bend forward and back, left and right from a standing position, raise your arms up, behind your head and stretch your abdominal muscles.At the same time, absolutely all therapeutic exercises are performed under the supervision of a specialist.
What to do if you suspect osteoarthritis?
Radiculitis is an extremely dangerous disease that most people often do not pay attention to.The danger of radiculitis lies in the fact that without the necessary treatment, the disease can cause the most unpleasant consequences - even paralysis of the legs and curvature of the spine.
That is why when the first signs of the disease appear, it is necessary to consult an orthopedist, who will prescribe the optimal course of treatment.Remember, the sooner you start treatment, the faster you will achieve positive results and get your spine healthy again.